As you are probably already aware, SQL Server 2012 reached the end of support on July 12, 2022 and Windows Server 2012/2012 R2 will reach end of support on October 10, 2023. After these dates, these products will no longer receive security updates, non-security updates or bug fixes, nor will they receive technical support.
This leaves your on-premise systems at Risk!
If you’re using either or both of these products, you’ll need a plan to ensure on-going support and security for your systems. We can help!
On October 24th, we will be presenting “Microsoft cloud for Manufacturing”. Join us to get planning a more modern and secure solution for your business in the Fall of 2023.
“When you’re running an outdated operating system, you may be missing critical updates and patches, leaving your system vulnerable to instability and crashes. Limited Security: Outdated operating systems are also more vulnerable to security risks, as they may lack the latest security updates and patches. One of the most common ways that hackers target organizations is by exploiting vulnerabilities in outdated software. Outdated software risks can leave you open to a variety of hacks, including ransomware, malware, data breaches, and more.”
5 Risks Of Outdated On-premise Software & Operating Systems
- Security Risks: Outdated software leaves your systems vulnerable to the ever-increasing threat of cyber-attacks. Additionally, on-premise servers are physical assets and as such face the same dangers the rest of the building might be exposed to, including fires, floods, or break-ins.
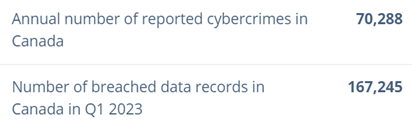
- Inability to Scale:
As companies grow, their data storage needs to change and expand. Scaling physical servers is costly and time-consuming, while cloud storage and computing resources can seamlessly scale to accommodate growing companies. If your software is already out-dated then you will be forced to upgrade, which can cause significant cost and interruption to your business.
- Minimal Data Backup & Recoverability:
The greatest risk for on-premise servers is the loss of data and the minimal backup and recovery options available. A malfunction in the system, or a compromised system held for ransom by a cyber “threat actor” can lead to a permanent loss of data on a company’s internal server. While businesses can choose to store their data on an off-site backup server, this service generates additional costs and maintenance fees. Additionally, most on-premise systems lack server redundancies (i.e. when one server goes down another kicks-in – this redundancy is included in Microsoft’s cloud systems).
- Increased Costs:
Keeping on-premise servers running and secure can generate a lot of extra costs, especially if no additional security\patch updates are being provided. This places additional time requirements on companies’ IT staff, making it even more necessary to have a dedicated IT support team. Between the maintenance costs of server hardware, power consumption, and accounting for the physical space the server occupies, on-premise servers end up costing companies more money in the long run.
- Lack of Secure Remote Access & Mobility for Employees:
Since the pandemic, businesses have been faced with the requirement to provide remote options for many, if not all of their employees. Ensuring employees have remote and mobile access to their data and systems is essential to keep things running smoothly and ensuring this access is secure is equally essential. Most on-premise remote access tools are not nearly as secure as they should be.
